How exactly does the treatment work?
Know what dry vapor technology is before understanding the process: click here. If you already know then continue on...
Peracetic Acid
(CH OOOH)
3
As a common disinfectant, Peracetic Acid does most of the heavy lifting. Upon completion of service, there will be no traces of Peracetic Acid left in the home or place of business.
Acetic Acid
(CH OOH)
3
Acetic acid is a household disinfectant. When mixed with water it becomes vinegar.
Hydrogen Peroxide
(H O )
2
2
Also commonly found in the home, Hydrogen Peroxide is used as an anti-septic for cuts and scrapes.
Step 1: InstaPure Process
Dry Vapor Application of Peracetic Acid (PAA) is Fast & Safe
All active ingredients used in this step are marked with a "Green Circle" (the best possible rating) on the
How They Work Together
H O
2
2
(Hydrogen Peroxide)
CH OOOH
3
(Peracetic Acid)
H O
2
(Water Vapor)
Still More
Hyrdrogen Peroxide?
Repeat
CH OOH
3
(Acetic Acid)
Yes
No
.png)
.png)
.png)
(Lysis)
O
2
(Stable Oxygen)
In a process called "lysis" the oxygen ruptures the cells and renders them inert.
When there is no more Hydrogen Peroxide left in the fog the reactions stop and we are left with only Acetic Acid, water vapor, and stable oxygen. The levels are safe for anyone to reenter before we leave.
When the oxygen leaves
Peracetic Acid becomes Acetic Acid. It then reacts with Hydrogen
Peroxide to create more Peracetic Acid. The leftover molecule is
water vapor.
CH OOOH
3
(Peracetic Acid)
CH OOH
3
(Acetic Acid)
O
(Oxygen)
Once mixed with water and released in our fog, one oxygen atom breaks off the Peracetic Acid and "hunts down" bacteria and mold spores.
Step 2: The EverPure Process
Preventing Future Mold Growth
As the backbone of our warranty, this step uses mechanical means, not chemical reactions, to protect your home after we leave.

Untreated Surface
The treated
area creates a surface that
attracts and destroys microbes.
-
After treatment all surfaces have
an anti-microbial layer with
microscopic spikes facing outward.
-
With a single Nitrogen atom, each of the
spikes has a positive electrical charge.
-
Microbes (such as mold and bacteria)
are negatively charged and
attracted to the spikes like magnets.
-
Upon impact the spikes tear the cells apart.
Treated Surface
The process can be viewed in this video.
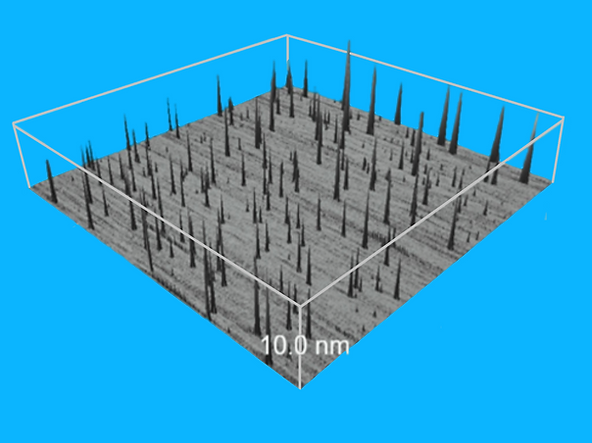
They may look intimidating, but you'll never know these spikes are there. There is no residue, texture, or chemical release. And at 1/1,000 the size of human hair they are incredibly tiny.
So tiny, in fact, you can fit almost
500 trillion on the surface of a quarter.
.png)
%20Grouped_edited.png)